Er Diagram Question And Solution Pdf Download
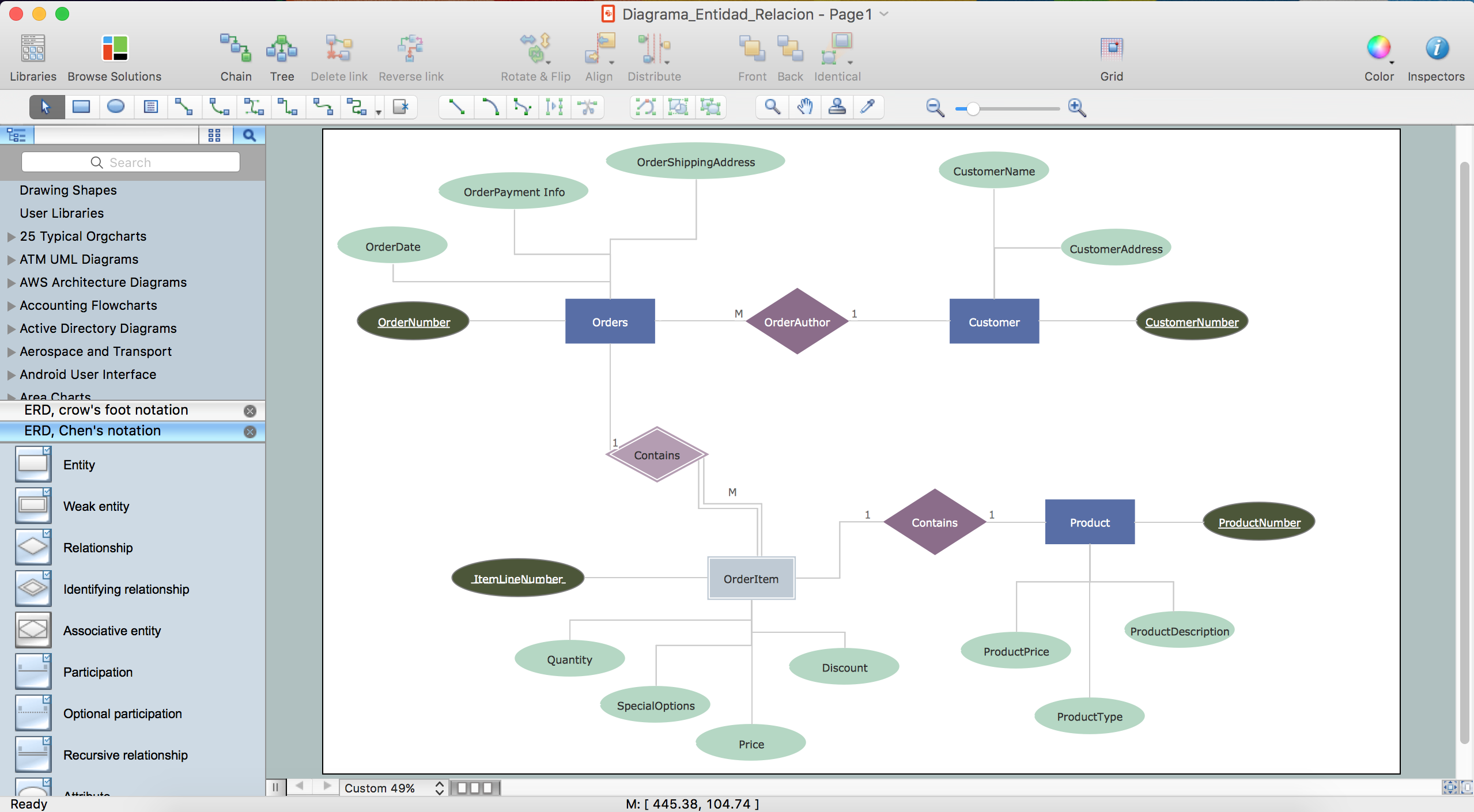
Download full-text PDF. ER-diagrams, is effectively a set of diagrammatic primitive. Students to provide good solutions to the first question (they did). Examples of UML diagrams - website, ATM, online shopping, library management, single sign-on (SSO). UML Diagrams Examples Examples by Technology or Application Domain. Software licensing and protection using SafeNet Sentinel HASP security solution Examples by Types of Diagrams Activity diagram examples Class diagram examples. APPROPRIATE ER MODEL DESIGN Choose names that convey meanings attached to various constructs. Nouns give rise to entity type names Verbs indicate names of relationship types.Choose binary relationship names to make ER diagram readable from left to right and from top to bottom Review all attributes.
In plastic analysis and design of a structure, the ultimate load of the structure as a whole is regarded as the design criterion. The term plastic has occurred due to the fact that the ultimate load is found from the strength of steel in the plastic range. This method is rapid and provides a rational approach for the analysis of the structure. It also provides striking economy as regards the weight of steel since the sections required by this method are smaller in size than those required by the method of elastic analysis. Plastic analysis and design has its main application in the analysis and design of statically indeterminate framed structures.
The discussion in the previous sections focused mainly on simple indeterminate structures. Typically, these structures have n degrees of indeterminacy and require n + 1 number of plastic hinges to form a collapse mechanism.
In such cases, the structures are said to have failed by complete collapse. We define complete collapse as When a structure with n degrees of indeterminacy collapses due to the formation of p number of plastic hinges where p ¼ n + 1, the structure fails by complete collapse; in this case, determination of the member forces for the whole structure at collapse is always possible.
However, partial collapse of a structure can be defined as When a structure with n degrees of indeterminacy collapses due to the formation of p number of plastic hinges where p. Contrary to the traditional thinking that plastic analysis is performed either by simple manual methods for simple structures or by sophisticated computer programs written for more general applications, this book intends to introduce general plastic analysis methods, which take advantage of the availability of modern computational tools, such as linear elastic analysis programs and spreadsheet applications. These computational tools are in routine use in most engineering design offices nowadays. The powerful number-crunching capability of these tools enables plastic analysis and design to be performed for structures of virtually any size. The amount of computation required for structural analysis is largely dependent on the degree of statistical indeterminacy of the structure. For determinate structures, use of equilibrium conditions alone will enable the reactions and internal forces to be determined.
For indeterminate structures, internal forces are calculated by considering both equilibrium and compatibility conditions, through which some methods of structural analysis suitable for computer applications have been developed. The use of these methods for analyzing indeterminate structures is usually not simple, and computers are often used for carrying out these analyses. Most structures in practice are statically indeterminate. The flexibility method is used to solve equilibrium and compatibility equations in which the reactions and member forces are formulated as unknown variables.
Er Diagram Question And Solution Pdf Download Software
In this method, the degree of statiscal indeterminacy needs to be determined first and a number of unknown forces are chosen and released so that the remaining structure, called the primary structure, becomes determinate. The primary structure under the externally applied loads is analyzed and its displacement is calculated. A unit value for each of the chosen released forces, called redundant forces, is then applied to the primary structure (without the externally applied loads) so that, from the force-displacement relationship, displacements of the structure are calculated. The structure with each of the redundant forces is called the redundant structure. The compatibility conditions based on the deformation between the primary structure and the redundant structures are used to set up a matrix equation from which the redundant forces can be solved.